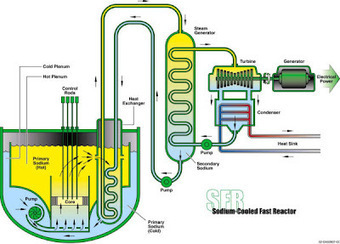
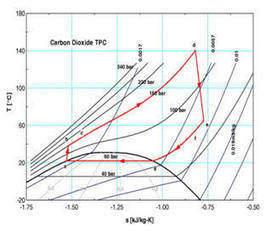
See on Scoop.it – Green Energy Technologies & Development
The new power plant unit, Brista 2, produces district heat for local residents and electricity for the Nordic power market from sorted municipal and industrial waste.
>”Brista 2 is already the fourth CHP plant we have commissioned this year in the Nordic and Baltic countries. Combined heat and power production is at the core of our strategy, and whenever possible we utilise renewable and local fuels,” says Per Langer, Executive Vice President of Fortum’s Heat Division.
Production capacity of the new Brista plant unit is 60 megawatts (MW) heat and 20 MW electricity. The annual heat production, about 500 gigawatt-hours (GWh), corresponds to the annual heating needs of about 50,000 mid-sized homes. The estimated annual electricity production of Brista 2 is 140 GWh. Fortum co-owns the plant (85%) together with the municipal energy company Sollentuna Energi (15%). <
See on online.wsj.com