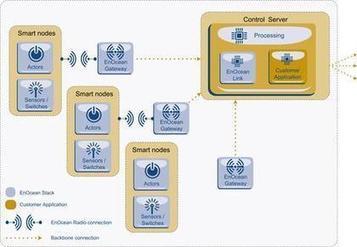
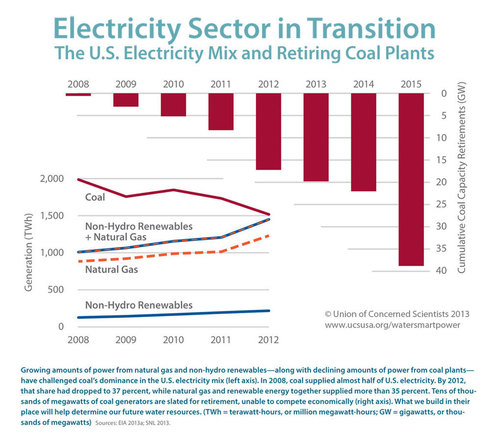
See on Scoop.it – Green & Sustainable News
By SEN. JEANNE SHAHEEN and SEN. ROB PORTMAN | 7/29/13 9:25 PM EDT
For the past three years, we have worked together to develop the Energy Savings and Industrial Competitiveness Act, legislation that will go a long way toward making the United States more energy efficient and more economically competitive.
According to the Sen. Shaheen & Portman:
>Our bill curbs inefficient energy practices that cost the U.S. economy billions of dollars and millions of jobs every year. According to a recent study by the Emily Hall Tremaine Foundation, we waste an astonishing 86 percent of the energy we consume. Upgrading the energy efficiency of U.S. buildings alone could save $1 trillion over the next decade. Cutting down on energy waste represents an untapped resource that we have long ignored. Our legislation helps to change that.
Our bill promotes energy savings that Americans across the political spectrum can get behind. Energy efficiency has broad, bipartisan support from business, energy and environmental advocates alike, and the legislation we have developed helps to promote energy efficiency through a smart, pragmatic plan that can be implemented immediately.
There is one mandatory component to the bill: We are going to make Washington practice what it preaches. We’re going to make the federal government — the largest energy user in the country — adopt energy-saving techniques and best practices that make its operations more efficient. […]
These provisions will save money, make America more energy-independent and lower harmful emissions. For the private sector, the tools our bill deploys are entirely voluntary. This legislation will also not add to the deficit and its costs are fully offset.<
See on www.politico.com