See on Scoop.it – Green & Sustainable News
Learn how the China water crisis will have significant impact on the balance of the world if not reversed, and how you can help, in this WaterFilters.NET post.
>The New York Times reports:
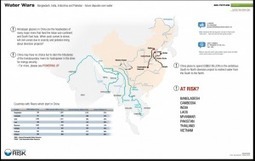
Beijing has placed its faith in monumental feats of engineering to slake the north’s growing thirst. The South-North Water Transfer eventually aims to pipe 45 cubic kilometers of water annually northward along three routes in eastern, central and western China. All three pose enormous technical challenges: The eastern and central routes will be channeled under the Yellow River, while the western route entails pumping water over part of the Himalayan mountain range.
The estimated cost of $65 billion is almost certainly too low, and doesn’t include social and ecological impacts. Construction has already displaced hundreds of thousands, and issues the like possible increases in transmission of water-borne diseases have not been properly studied. But Beijing’s calculus is political: It is easier to increase the quantity of water resources, at whatever cost, rather than allocate a limited supply between competing interests. […]
A recent article by The Economist states:
“The Chinese government would do better to focus on demand, reducing consumption of water in order to make better use of limited supplies. Water is too cheap in most cities, usually costing a tenth of prices in Europe. Such mispricing results in extravagance. Industry recycles too little water; agriculture wastes too much. Higher water prices would raise costs for farms and factories, but that would be better than spending billions on shipping water round the country.”
Economically supporting Chinese regions and corporations that commit to better water usage and sustainability practices may help to change the mindset of many within this nation’s government or industries. In turn, this could lead them towards exploring more realistic initiatives experiencing success in other parts of the world.<
See on blog.waterfilters.net