Author: Duane M. Tilden, P.Eng (January 14th, 2016)
Abstract: Energy sources and pricing are hot topics world-wide with the Climate Change agenda leading the way. Last year at the 2015 Paris Climate Conference long-term goal of emissions neutrality was established to be by as soon as 2050. Alberta currently produces more atmospheric carbon emissions and other pollutants than any other Province in Canada, and in order to meet clean air objectives the energy sectors which consume & mine the natural resources of the Province will have to shift to non-polluting & renewable energy sources and be more efficient in energy utilization. To achieve these goals new infrastructure will have to be built which will have the likely consequences of raising energy pricing as well as alter consumption rates and patterns.
Transportation
Transportation is a vital link in modern society, and often a personal vehicle is chosen as the main mode of mobility to work, leisure, & social purposes. Cars and trucks also provide means of work and commerce & are essential to our way of life. Most of these vehicles are fueled by gasoline, some by diesel, propane, and more recently the electric vehicle (EV) and hybrids.

Graph #1: Average Cost Comparison of Gasoline in Major Canadian Cities
In Alberta, using Calgary as a basis for comparison, it is apparent that pricing to consumers for gasoline is below nation-wide market averages when measured Province by Province, as demonstrated in Graph #1 (1). While if you live in Vancouver the cost is considerably higher, due to included carbon taxes and a transit levy among additional charges. Additional means of moving growing populations efficiently have been seen by the development of LRT mass transit for the rapid movement of citizens to work, school, or social events.
Rapidly moving the large segments of the population in a cost effective manner is important to growth. Buses are an important link in this mix as are cycling routes, green-ways and parks. Changes in fuels for trucks, buses and trains by converting from diesel fuel to LNG will also provide for reductions in emissions while providing economic opportunity for utilization of the existing plentiful resource. While EV’s show promise, the battery technologies for energy storage need further development.
Alberta Electricity Production
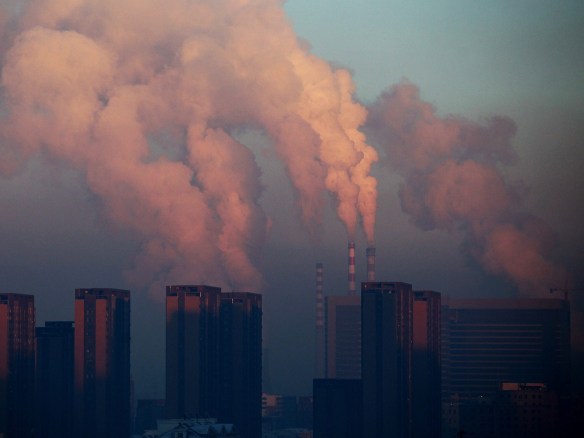
Alberta still relies on out-dated coal plants to generate electricity. According to a CBC article coal provides power to 55% of homes in Alberta, and is the second largest contributor to emissions (2) and GHG’s to the Oil Sands projects. However, it has been noted that the utility is reluctant to decommission recently constructed coal plants, until they have earned back (or are compensated for) their investment in capital costs.

Photo #1: Highvale coal mine to feed the nearby Sundance power plant (3)
Photo credit: John Lucas / Edmonton Journal
There are power purchase agreements in place, which may extend 50 to 60 years from the construction date of the plant (2). It may be possible that the coal fired power plants could be converted to burn natural gas, which Alberta has in abundance, rather than be decommissioned. However, this would still require the closure of the coal mines and mining operations currently supplying the existing power plants. Also, combustion of natural gas will still release GHG’s into the atmosphere, while less than coal, they are not a total elimination of emissions.
Residential Energy Consumption
When comparing monthly residential electrical energy costs across Canada, using data obtained from a survey performed by Manitoba Hydro, we see that Edmonton and Calgary are in the lower middle range of pricing (4). Variances in all regions will occur based on average home size, building codes and insulation requirements, heating system types and other factors. Some homes may be heated with electric baseboard which will result in a higher electric bill while other homes may be heated using natural gas as a fuel. Also household hot water generation can be by electric or gas-fired heater, so consumption of natural gas must be considered with electrical power usage to get a complete picture of energy consumption.


Charts #1 & 2: Average Monthly Cost For Residential Electricity in Major Canadian Cities For Equivalent Usage in kWh (4)
Inspecting these charts it is proposed that a price increase of 10 to 20% to Alberta electrical energy consumers by a separate tax or fee to pay for a shift in technology would be reasonable when compared to other Canadian Cities. Additional tariffs on natural gas consumption would also be recommended. Such an increase would likely have a secondary benefit of creating an incentive for energy efficiency upgrades by home owners such as increased insulation, better windows and heating system upgrades. Such improvements would in turn lead to reduced demand at the source and thus to lower GHG & particulate emissions to the atmosphere.
Climate and the Proposed Energy Code
Energy consumption in populations is normalized in a number of ways, generally defined by habits and patterns. We observe that in traffic as volumes increase early in the morning as commuters travel to work, and in the opposite direction as they head home in the evening. Often people will attempt to “beat the traffic”. This is an admirable goal in energy usage as well, for consumption of electricity will follow other such predictable patterns as people eat meals, shower, and perform other rituals that interface with electrical, heating, ventilating, elevators, water supply and disposal systems that form infrastructure and services provided by municipalities and utilities.
As these systems need to be energized and maintained, it is desirable to be able to predict and control the consumption and distribution of resources. The greater of these is the electrical generation and distribution system. Also, emerging technological advancements in energy efficiency such as CFL, LCD displays, computers, refrigeration, energy storage and more. Advancements in co-generation, district energy systems, and other end use distribution of energy which provide economies of scale are also possible as strategies to obtain goals.
Map #1: Partial Map of Heating Degree Days for South-Western Canada (5)
Opportunities will exist for building mechanical system enhancements and upgrades as they may provide energy savings and cost reductions to users often calculated with a minimum nominal payback period of 5 to 7 years (and should be determined in every case). The HDD map can provide a source of information which is used in energy models to determine predicted building energy costs when calculating payback periods to justify system upgrades or design decisions. Obtaining and monitoring building energy consumption rates and year over year changes are important resources in determining where systems are running at below optimal rates and require replacement.
In new building construction the National Energy Code for Buildings 2011 (NECB) (6) has been adopted by Alberta (7) for all municipalities. As there are higher HDD values attributed to Calgary and Edmonton as seen in the HDD Map of Western Canada, a requirement for stringent construction methods and materials to higher standards ensure new buildings meet carbon emissions reduction goals.

Photo #2: Construction of Towers in Calgary with High Window to Wall Ratios
Photo Credit: Duane Tilden P.Eng
Increased requirements in glass U-values and shading coefficients, maximum window to wall ratios (WWR) to reduce undesirable solar heat gain and heat losses, energy consumption and improve occupant comfort. Buildings with excessive glazing are difficult to heat and cool, requiring sophisticated mechanical systems to offset poor performance by the building envelope.
Code mandated higher insulation values & better materials; moisture and heat control of the envelope through better design. Higher efficiency requirements for mechanical systems; (fans & ducts, pumps & pipes, and wires & motors), lighting, controls, and other components of the building and it’s envelope. Energy modeling should be performed of larger significant buildings to optimize operations in the design phase. Commissioning of the building is integral to ensuring compliance throughout the project to it’s final phases at substantial completion and occupancy.
Renewable Energy
Renewable energy technologies including solar power and wind generation have been gaining rapid adoption elsewhere in the world, while in Alberta (8) carbon based fuels currently provide over 80% of electrical power generation. This has not been for a lack of wind and solar resources in Alberta but to be attributed to the large capital investments in fossil fuel resource extraction. Other renewable technologies such as bio-mass, hydro, and geothermal may also be employed and should be investigated as alternatives to existing thermo-electric power plants.
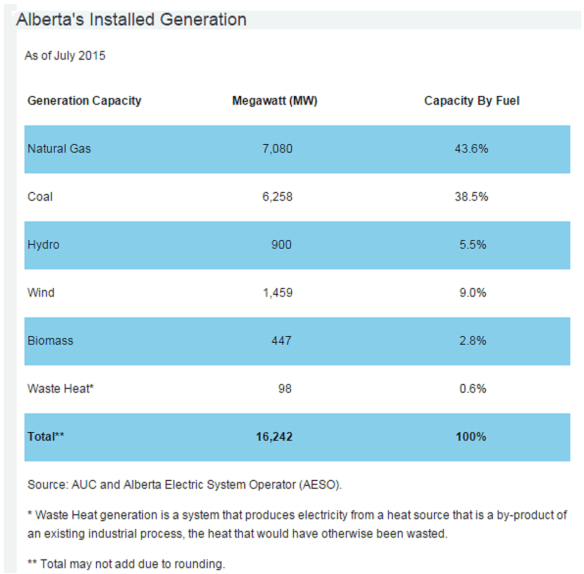
Table #1: Installed Electrical Generating Capacity by Fuel Source in Alberta (8)
Currently, Alberta has the third highest installed wind power capacity in Canada behind Ontario and Quebec. Wind energy not only represents a means to green the power production, it also will contribute jobs and income to the economy. As one source of electricity and revenues is removed another source will fill the void.
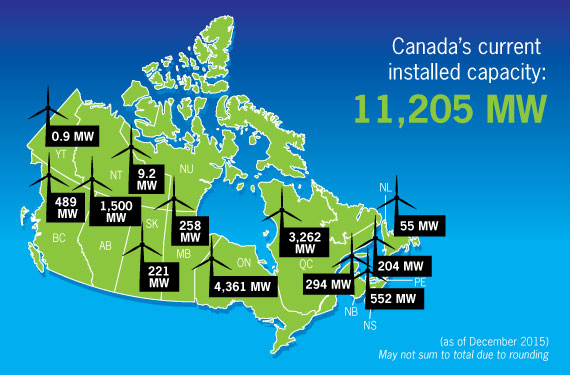
Map #2: Installed Wind Power Capacity by Province in Canada (9)
While significant inroads have been made in Alberta for wind power which is already established as a major power source for the future, there is unrealized potential for the installation of solar power production. It has been noted that a photo-voltaic installation in Calgary is 52% more efficient than one installed in Berlin, Germany. Meanwhile, Germany has 18,000 times more solar power generation capacity than installed in Alberta (10).

Map #4: Solar Resource Comparison for Alberta & Germany (10)
Alberta has significant solar resources, even during the winter when daylight hours are shorter. Lower temperatures improve PV efficiency, and properly tilted south facing panels optimize light capture, while the flat terrain of the prairies provide unobstructed maximum daylight. Light reflection by snow on the ground would further enhance light intensity during the colder months. Thus solar represents a relatively untapped potential source of significant electrical power for Alberta and an unrealized economic opportunity for consumers and industry.
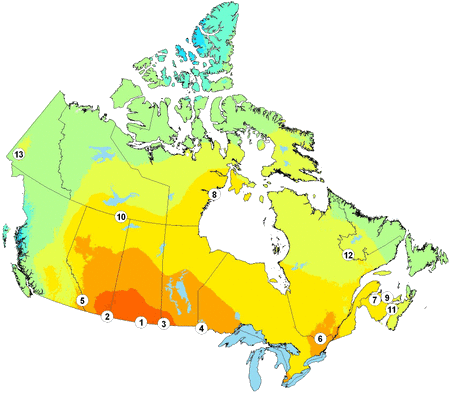

Map #5: Solar Resource Map for Canada With Hotspots (11)
Energy Efficiency, Smart Grid & Technological Advancements
Renewable energy produces electricity from natural resources without generating carbon and particulate emissions. Another method of controlling emissions is to reduce the amount of energy consumed by being more efficient with the energy we already produce. We can achieve this by using higher efficiency equipment, changing consumer patterns of use to non-peak periods, use of Smart Meter’s to monitor consumer usage and to alert homeowners when there is a problem with high consumption which could result in higher bills than normal if the problem remained unreported.
There are other advancements in the electrical grid system which are on the horizon which will enable a utility maximize resources by such means as energy storage, micro-grids, demand response to name a few. Also, property owners and businesses could be able to grid-tie private solar panel (PV) and storage systems to supplement the utilities electrical system with additional power during the day.
Summary
In order to meet the goal of atmospheric emissions neutrality as agreed to at the 2015 Paris Climate Conference Alberta is posed with making decisions on how electricity is to be produced in the future. Eliminating coal power plants and replacing them with Renewable Energy power sources such as solar and wind power are proven methods to reducing GHG and particulate emissions as these power sources do not involve combustion and discharge of waste gases formed during the combustion process. Coal combustion is well documented as a major contributor of GHG’s to the atmosphere.
To make the transition will require capital for financing to build new infrastructure. Funding of these projects should be raised proportionally charged to users with increased rates. These rate increases will provide further incentives to reducing energy consumption and thus air emissions. Jobs will shift and employment will be created in new forms as the old is phased out and replaced with new technology. These new systems will have to be designed, built and maintained while the workforce will require training in new methods. There will be many new opportunities for growth and advancement resulting from the implementation of these changes to meet Canada’s International commitments.
References:
- http://www.nrcan.gc.ca/energy/fuel-prices/4593
- http://www.cbc.ca/news/business/coal-compensation-power-alberta-1.3321467
- http://edmontonjournal.com/business/local-business/albertas-commitment-to-phase-out-coal-fired-power-sparks-fears-of-job-losses
- https://www.hydro.mb.ca/regulatory_affairs/energy_rates/electricity/utility_rate_comp.shtml
- http://ftp2.cits.rncan.gc.ca/pub/geott/atlas/archives/english/5thedition/environment/climate/mcr4033.jpg
- http://www.nrc-cnrc.gc.ca/eng/publications/codes_centre/necb_2011_adaptation_guidelines.html
- http://www.municipalaffairs.alberta.ca/CP_Energy_Codes_Information
- http://www.energy.alberta.ca/electricity/682.asp
- http://canwea.ca/wind-energy/installed-capacity/
- http://www.greenenergyfutures.ca/blog/sunny-days-ahead-solar-alberta
- http://pv.nrcan.gc.ca/index.php?lang=e&m=r































