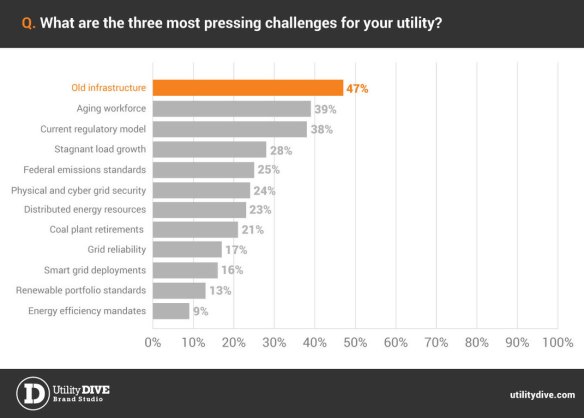
The State of the Electric Utility 2015 survey revealed that aging infrastructure is what troubles industry players most.
Source: www.utilitydive.com
>” Utility executives identified aging infrastructure as the number one challenge facing the electric industry, […] easily topping an aging workforce, regulatory models and stagnant load growth. In response, the industry is spending hundreds of billions to replace and upgrade infrastructure, rushing to meet consumer demand for higher quality power enabled by construction of a more modern grid.
“The last few years there’s been more of an emphasis on transmission and distribution, and the driver there has been the advent of all these new technologies that are trying to connect with the grid,” said Richard McMahon, Jr., vice president of energy supply and finance for the Edison Electric Institute, the electric utility trade organization. “There are also a lot of customer-driven desires utilities are trying to facilitate. There’s a lot of spending on metering automation, as well as at the distribution level, distribution transformers to accommodate distributed generation.”
Today’s grid may not be up to the task of reliably integrating high levels of renewables, distributed energy resources, and smart grid technologies, Utility Dive found. The American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE) gave U.S. energy infrastructure a barely passing grade of D+ in 2013, at stark odds with the sophisticated grid management required by the rapid acceleration of utility-scale renewables, distributed resources and two-way devices.
“Distributed energy cannot be a profit center without the modernized grid infrastructure that’s needed for grid integration,” Utility Dive concluded in the report. […]
Outages on the rise
The American Society of Civil Engineers report that gave U.S. infrastructure a barely-passing grade pointed out that aging equipment “has resulted in an increasing number of intermittent power disruptions, as well as vulnerability to cyber attacks.”
Significant power outages rose to more than 300 in 2011, up from about 75 in 2007, and the report found many transmission and distribution outages have been attributed to system operations failures, though from 2007 to 2012 water was the primary cause of major outages.
“While 2011 had more weather-related events that disrupted power, overall there was a slightly improved performance from the previous years,” the report said. “Reliability issues are also emerging due to the complex process of rotating in new energy sources and ‘retiring’ older infrastructure.
ASCE said that for now, the United States has sufficient capacity to meet demands, but from 2011 through 2020 demand for electricity in all regions is expected to increase 8% or 9%. The report forecasts that the U.S. will add 108 GW of generation by 2016.
“After 2020, capacity expansion is forecast to be a greater problem, particularly with regard to generation, regardless of the energy resource mix,” the report said. “Excess capacity, known as planning reserve margin, is expected to decline in a majority of regions, and generation supply could dip below resource requirements by 2040 in every area except the Southwest without prudent investments.” […]”<
See on Scoop.it – Green & Sustainable News
Reblogged this on Milieunet.
LikeLiked by 1 person